Follow the Gap
Introduction
This lab is about the implementation of reactive algorithm to make the car drive autonomously around the Levine Hall map and meanwhile avoiding obstacles. There are many reactive algorithms the f1tenth car can use, which are follow the wall algorithm(which is implemented in this lab), TangentBug algorithm, potential field algorithm, etc.. Each algorithm has its unique disadvantage. As for follow the gap, it has a risk of doing a U-turn when encountering obstacle; for TangentBug, it is prone to take long trajectory towards the goal and it occasionally gets too close to the obstacles; for potential field, it may be trapped in the local minima with gradient descent.
Follow the Gap Algorithm
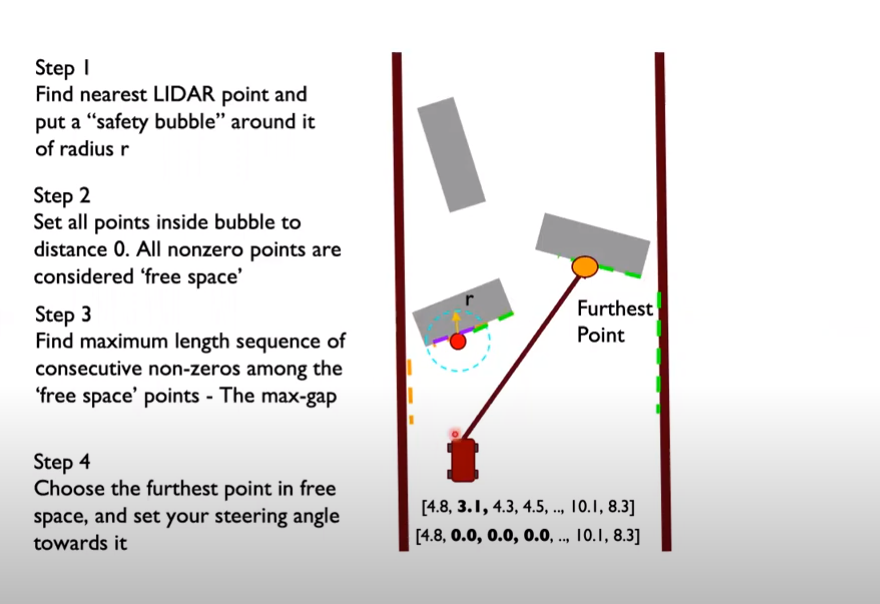
- step 1: Find the nearest LIDAR point and put a “safety bubble” around it of radius rb(radius of robot)
- step 2: Set the LaserScan range value of all points inside bubble to distance 0. All nonzero points are considered “free space”
- step 3: Find maximum sequence of consecutive non-zeros among the free-space points. This is the maximum gap where the car can drive towards.
- step 4: Find the best point among this maximum gap(naive way is choose the furthest point in free space and set steering angle towards it)
Implementation Explanation
My implementation of the follow the gap node consists of these steps(each step corresponds to that in the above algorithm):
- step 1: Process LaserScan and set field of view of 100 degrees(50 to the left and 50 to the right), beyond this range, set the LaserScan range value to 0(m). Using a sliding 1D convolution window [0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2] to make a moving average of LaserScan range. Clipping all value between [0, 4] Find the minimum range value(closest_dist) and its angle(closest_angle) after doing above steps.
- step 2: Make for loop, calculate the distance from the end of each LaserScan to the closest point by calculating the length of the arc (closest_dist * abs(angle_i - closest_angle)). If its length of arc is less than radius of robot, set its range value to 0.
- step 3: Find the max gap, the maximum sequence of consecutive non-zeros of the range array.
- step 4: Find the angle with the largest range value within the max gap. Set steering angle to be exactly this angle.(If there are several angles with largest range value, set steering angle with the minimum absolute value). Velocity depends on the range value of the furthest point. you can refer to the video below.
My Demo
The reactive planning node is written with rospy.
Related Learning Resources
UV F1/10 course Video:
Upenn F1/10 course Video: